- Forest Insights
With Latest Fires Crisis, Indonesia Surpasses Russia as World’s Fourth-Largest Emitter

By Nancy Harris, Susan Minnemeyer, Nigel Sizer, Sarah Alix Mann and Octavia Payne New analysis reveals even more troubling news about Indonesia’s fires crisis. Emissions from this year’s fires have reached 1.62 billion metric tons of CO2—bumping Indonesia from the sixth-largest emitter in the world up to the fourth-largest in just six weeks. The analysis from Guido van der Werf with the Global Fire Emissions Database also reveals that:
- Emissions from Indonesia’s fires alone are approaching the total annual emissions of Brazil.
- Indonesia’s current total emissions hover around 760 Mt CO2 (excluding land-use change), meaning the fires alone have tripled Indonesia’s entire annual emissions.
Indonesian fires during 38 of the past 56 days (as of October 26) have released more greenhouse gas emissions than the entire U.S. economy on those days.
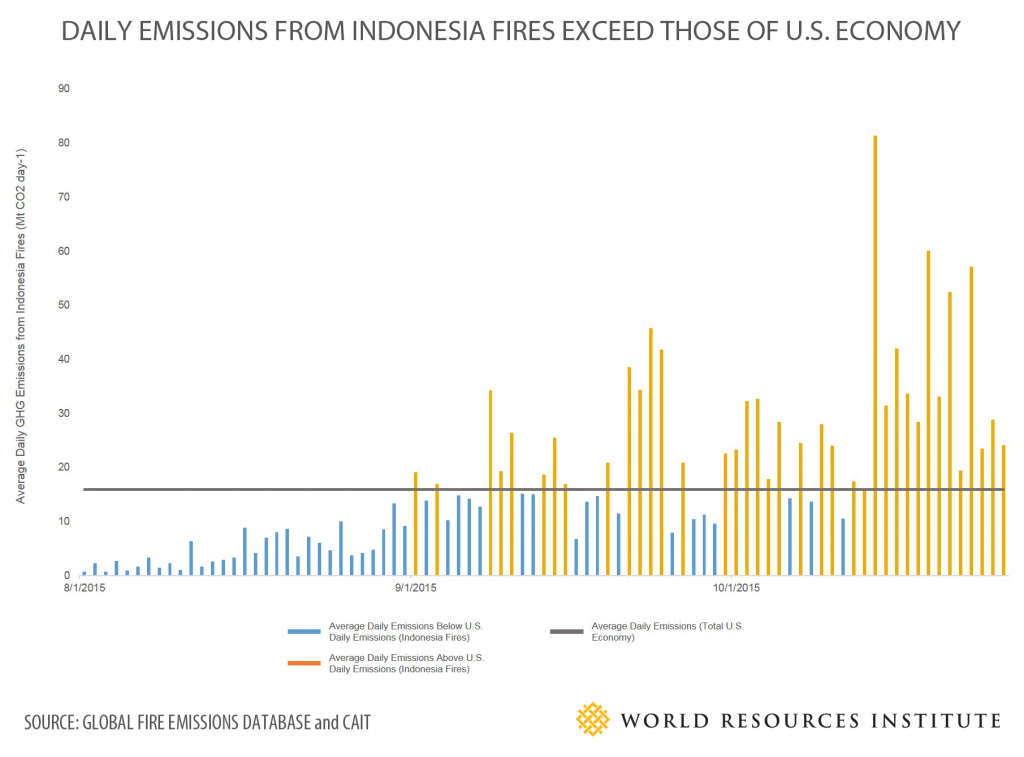
While the country may finally be getting some relief as heavy rainfall interrupts months of record-breaking fires and toxic smog in South Sumatra and Kalimantan, the damage to human health, the economy and the global climate has already been done.
Spurring a Climate Crisis
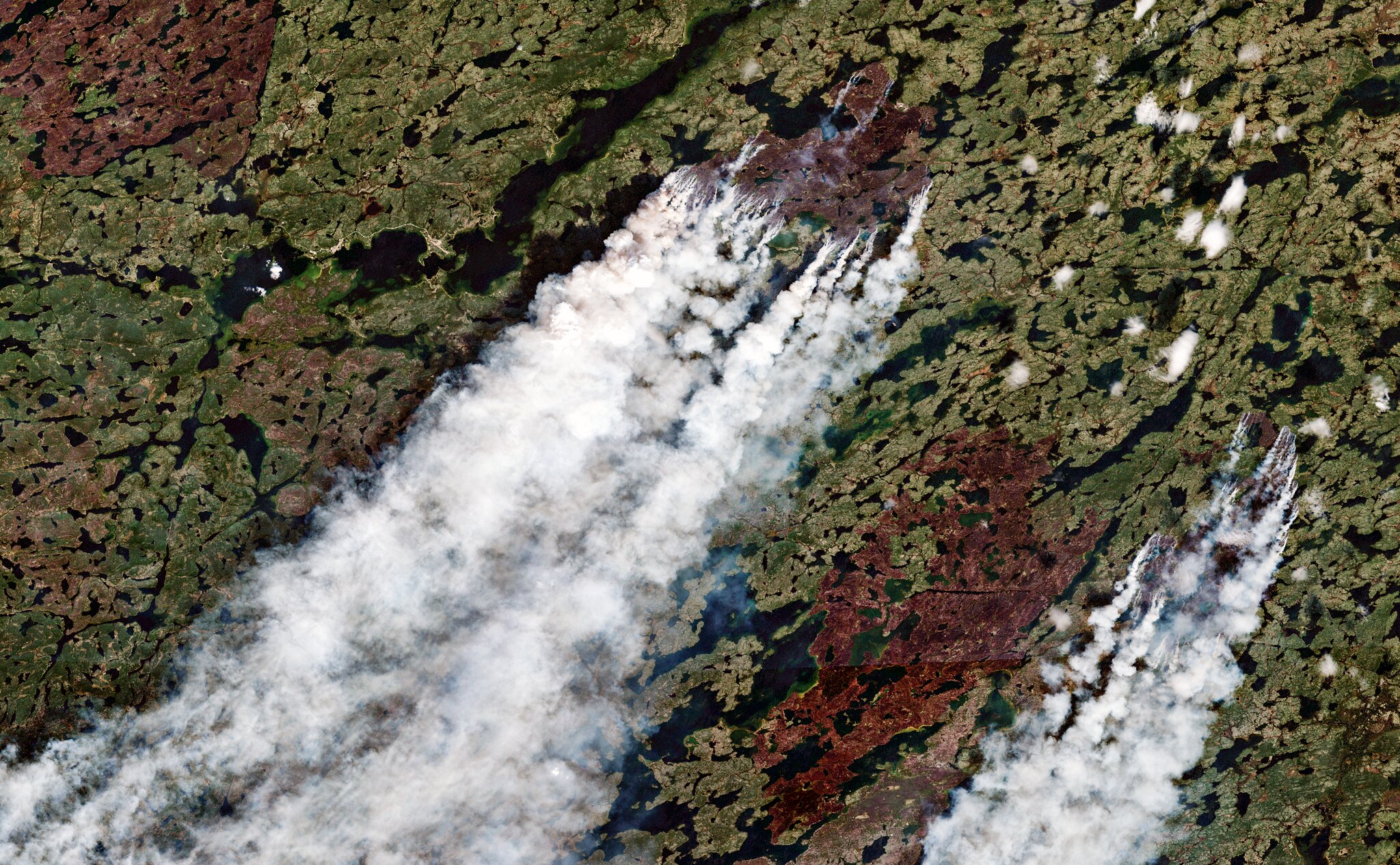
Global Forest Watch Fires has detected over 127,000 fires across Indonesia this year, the worst since 1997. Many of these fires were the result of clearing forested peatlands to make way for plantations of commodities such as palm oil. Much of the clearing and burning has been financed by small and medium sized investors.Peat stores some of the highest quantities of carbon on Earth and also emits methane resulting in up to 200 times more damage to the global climate than regular fires of similar extent. The smog is especially toxic. The impacts of these fires are especially significant in the run-up to the global climate conference in Paris at the end of this year. Deforestation usually constitutes about 60 percent of Indonesia’s total emissions, and the country has pledged to reduce deforestation and cut annual emissions by 29 percent from business as usual by 2030. The country will be unable to achieve this target if it does not take serious steps to quell existing fires and to prevent future fire outbreaks.
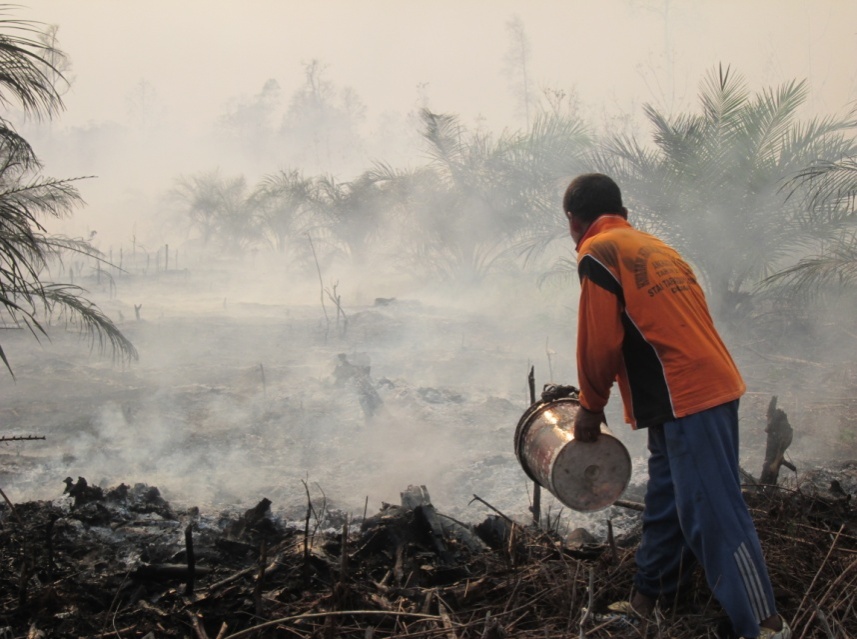
Fires Cause Human Casualties
An ounce of prevention There’s a human toll, too. As a result of these fires, toxic smog has enveloped a wide area across Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore, reaching as far as Thailand and the Philippines, closing schools, disabling airports, and forcing six Indonesian provinces to declare a state of emergency. Haze from this year’s fires likewise caused more than 500,000 cases of haze-related respiratory illnesses in Southeast Asia and resulted in the deaths of at least 19 Indonesians. Many more will die from the longer term impacts of breathing the foul air for weeks on end. All told, more than 40 million Indonesians have been affected. Experts from WRI and Global Forest Watch have already suggested three clear ways Indonesia can respond to this crisis and reduce the risks of future fires. In brief, we recommend:
- Adopting responsible financial incentives to commodity growers, so as to encourage more sustainable production of forest-based commodities;
- Focusing technical and mapping support on systems that harmonize land use management and reduce land conflicts; and
- Streamlining the murky world of concession licenses through innovative technologies that improve transparency and combat corruption in land use decision-making.
Indonesia desperately needs to take advantage of the hopeful respite provided by the rain to fast track reforms. Quick action is the only way to ensure that next year does not bring a repeat of this local and global calamity.


